Obsah
1. Validace dat v Pythonu s využitím knihovny Pydantic (3. část – dokumentace)
2. První varianta demonstračního datového modelu
3. Otestování demonstračního příkladu: načtení dat s jejich následným exportem
5. Ukázka vyexportovaného schématu před a po jeho naformátování
6. Export schématu ve formátu OpenAPI
7. Ukázka vyexportovaného schématu před a po jeho naformátování
8. První pokus o načtení schématu do SwaggerEditoru
9. Změna atributu exclusiveMinimum na minimum
10. Druhý pokus o načtení schématu do SwaggerEditoru
11. Špinavý trik s opravou definice volitelných atributů
12. Třetí (úspěšný) pokus o načtení schématu do SwaggerEditoru
13. Vygenerování dokumentace ve formátu Markdown
14. Přidání popisků k jednotlivým atributům modelu
15. Úplný zdrojový kód příkladu s popsaným modelem
16. Dokument se schématem, které má popsány všechny atributy
17. Převod na HTML stránku či na jiný typ dokumentu
19. Repositář s demonstračními příklady
1. Validace dat v Pythonu s využitím knihovny Pydantic (3. část – dokumentace)
Na úvodní dva články o knihovně Pydantic [1] [2] dnes navážeme. Prozatím jsme si popsali způsob definice (datového) modelu, jeho načítání a ukládání a samozřejmě i způsob validace, zda jsou všechny atributy (a vůbec celá struktura modelu) korektní. Ovšem ještě si musíme ukázat další velmi důležitou techniku – způsob automatického vygenerování dokumentace k modelu nebo modelům (to znamená i volbu formátu dokumentace atd.).
Jedná se o oblast, která vyžaduje kombinaci možností nabízených knihovnou Pydantic s dalšími nástroji (a navíc i několika triky). Výsledkem může být dokumentace ve formátu specifikace OpenAPI (tu dokážou zpracovávat různé nástroje) nebo dokument ve formátu Markdown (který lze pochopitelně naimportovat do textových procesorů, systémů pro správu obsahu včetně Confluence atd.), popř. dokument převedený z Markdownu do dalších formátů (HTML atd.).
2. První varianta demonstračního datového modelu
V dalších kapitolách budeme pracovat s relativně jednoduchým datovým modelem, který později vylepšíme přidáním popisků k jeho jednotlivým atributům. V knihovně Pydantic jsou všechny modely přímo či nepřímo odvozeny od třídy BaseModel:
from pydantic import BaseModel
My ovšem budeme požadovat, aby vstupní data, která datový model reprezentuje, neobsahovala žádné atributy navíc. Z tohoto důvodu od třídy BaseModel odvodíme novou „základní“ třídu nazvanou ConfigurationBase, která sice obsahuje všechny vlastností původního základního modelu, ovšem navíc vyžaduje, aby model neobsahoval neznámé (předem nedefinované) atributy:
class ConfigurationBase(BaseModel):
"""Base class for all configuration models that rejects unknown fields."""
model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid")
Náš datový model bude popsán třídou pojmenovanou Configuration. Jedná se o zdánlivě jednoduchý model s pouhými dvěma atributy:
class Configuration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Global configuration."""
name: str
service: ServiceConfiguration
Ovšem při prvním pohledu na typy těchto atributů je zřejmé, že musíme dodefinovat ServiceConfiguration. Základní varianta této třídy může vypadat následovně:
class ServiceConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Service configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 8080
auth_enabled: bool = False
workers: PositiveInt = 1
database: DatabaseConfiguration
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_service_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check service configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
Ovšem stále ještě nejsme u konce, neboť zbývá dodefinovat typ atributu nazvaného database. Tento atribut je typu DatabaseConfiguration:
class DatabaseConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Database configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 5432
db: str
user: str
password: str
ssl_mode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE
gss_encmode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE
ca_cert_path: Optional[FilePath] = None
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_postgres_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check PostgreSQL configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
V tento okamžik již máme k dispozici všechny části dnešního prvního demonstračního příkladu, jehož úplný zdrojový kód vypadá následovně:
# Knihovna Pydantic
#
# - model s konfigurací obsahující čtyři atributy
# - jeden z atributů je tvořen dalším modelem
# - kontrola obsahu atributů po inicializaci modelu
# - zákaz inicializace modelu s neznámými atributy
import json
from typing_extensions import Optional, Self
from pydantic import (
BaseModel,
ConfigDict,
FilePath,
PositiveInt,
model_validator,
)
# PostgreSQL connection constants
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-SSLMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE = "prefer"
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-GSSENCMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE = "prefer"
class ConfigurationBase(BaseModel):
"""Base class for all configuration models that rejects unknown fields."""
model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid")
class DatabaseConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Database configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 5432
db: str
user: str
password: str
ssl_mode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE
gss_encmode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE
ca_cert_path: Optional[FilePath] = None
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_postgres_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check PostgreSQL configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class ServiceConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Service configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 8080
auth_enabled: bool = False
workers: PositiveInt = 1
database: DatabaseConfiguration
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_service_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check service configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class Configuration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Global configuration."""
name: str
service: ServiceConfiguration
def dump(self, filename: str = "configuration.json") -> None:
"""Dump actual configuration into JSON file."""
with open(filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
fout.write(self.model_dump_json(indent=4))
Programátoři, co nesnášíte BS, ale máte rádi business! Y Soft je česká firma s globálním dopadem (100+ zemí, 1M+ uživatelů a >100% meziroční růst). R&D úplně bez manažerů (130 developerů). Otevíráme 30 pozic pro Cloud a AI: Praha/Brno/Ostrava/remote. Zodpovědnost ano, mikro-management ne. Pojď někam, kde můžeš věci změnit.
3. Otestování demonstračního příkladu: načtení dat s jejich následným exportem
Výše uvedený příklad (resp. přesněji řečeno model, jenž je v něm definován) otestujeme relativně snadno. Načteme do modelu obsah tohoto souboru (ve formátu YAML) a následně budeme obsah modelu exportovat:
name: Service configuration #1
service:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 8080
auth_enabled: false
workers: 5
database:
host: db1.pg.com
db: test
user: test
password: 123qwe
Načtení tohoto souboru obstará následující kód využívající knihovnu yaml:
import yaml
def load_configuration(filename: str) -> Configuration:
"""Load configuration from YAML file."""
with open(filename, encoding="utf-8") as fin:
config_dict = yaml.safe_load(fin)
return Configuration(**config_dict)
Samotné načtení následované exportem dat je již otázkou dvou programových řádků:
configuration = load_configuration("config_10.yaml")
configuration.dump("config_10.json")
Výsledkem by měl být soubor config10.json s exportovaným modelem:
{
"name": "Service configuration",
"service": {
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 8080,
"auth_enabled": false,
"workers": 5,
"database": {
"host": "db1.pg.com",
"port": 5432,
"db": "test",
"user": "test",
"password": "123qwe",
"ssl_mode": "prefer",
"gss_encmode": "prefer",
"ca_cert_path": null
}
}
}
4. Export schématu modelu
Knihovna Pydantic umožňuje export schématu modelu (tj. popisu struktury dat) do formátu JSON. Postačuje zavolat metodu model_json_schema, která vrací slovník (dictionary) s popisem schématu modelu:
Help on method model_json_schema in module pydantic.main:
model_json_schema(by_alias: 'bool' = True, ref_template: 'str' = '#/$defs/{model}', schema_generator: 'type[GenerateJsonSchema]' = , mode: 'JsonSchemaMode' = 'validation') -> 'dict[str, Any]' class method of pydantic.main.BaseModel
Generates a JSON schema for a model class.
Args:
by_alias: Whether to use attribute aliases or not.
ref_template: The reference template.
schema_generator: To override the logic used to generate the JSON schema, as a subclass of
`GenerateJsonSchema` with your desired modifications
mode: The mode in which to generate the schema.
Returns:
The JSON schema for the given model class.
Následný export do formátu JSON je již snadný, protože pro tento účel můžeme použít standardní balíček json:
with open("schema_11.json", "w") as fout:
json.dump(Configuration.model_json_schema(), fout)
Upravme si tedy náš demonstrační příklad do takové podoby, aby po svém spuštění vytvořil soubor s popisem schématu modelu:
# Knihovna Pydantic
#
# - model s konfigurací obsahující čtyři atributy
# - jeden z atributů je tvořen dalším modelem
# - kontrola obsahu atributů po inicializaci modelu
# - zákaz inicializace modelu s neznámými atributy
# - export schématu modelu
import json
from typing_extensions import Optional, Self
from pydantic import (
BaseModel,
ConfigDict,
FilePath,
PositiveInt,
model_validator,
)
# PostgreSQL connection constants
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-SSLMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE = "prefer"
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-GSSENCMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE = "prefer"
class ConfigurationBase(BaseModel):
"""Base class for all configuration models that rejects unknown fields."""
model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid")
class DatabaseConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Database configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 5432
db: str
user: str
password: str
ssl_mode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE
gss_encmode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE
ca_cert_path: Optional[FilePath] = None
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_postgres_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check PostgreSQL configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class ServiceConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Service configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 8080
auth_enabled: bool = False
workers: PositiveInt = 1
database: DatabaseConfiguration
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_service_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check service configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class Configuration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Global configuration."""
name: str
service: ServiceConfiguration
def dump(self, filename: str = "configuration.json") -> None:
"""Dump actual configuration into JSON file."""
with open(filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
fout.write(self.model_dump_json(indent=4))
with open("schema_11.json", "w") as fout:
json.dump(Configuration.model_json_schema(), fout)
5. Ukázka vyexportovaného schématu před a po jeho naformátování
Soubor schema11.json se schématem, který jsme získali, má následující obsah:
{"$defs": {"DatabaseConfiguration": {"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "title": "Host", "type": "string"}, "port": {"default": 5432,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0, "title": "Port", "type": "integer"}, "db": {"title": "Db", "type": "string"}, "user":
{"title": "User", "type": "string"}, "password": {"title": "Password", "type": "string"}, "ssl_mode": {"default":
"prefer", "title": "Ssl Mode", "type": "string"}, "gss_encmode": {"default": "prefer", "title": "Gss Encmode",
"type": "string"}, "ca_cert_path": {"anyOf": [{"format": "file-path", "type": "string"}, {"type": "null"}],
"default": null, "title": "Ca Cert Path"}}, "required": ["db", "user", "password"], "title": "DatabaseConfiguration",
"type": "object"}, "ServiceConfiguration": {"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Service configuration.",
"properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "title": "Host", "type": "string"}, "port": {"default": 8080,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0, "title": "Port", "type": "integer"}, "auth_enabled": {"default": false, "title": "Auth Enabled",
"type": "boolean"}, "workers": {"default": 1, "exclusiveMinimum": 0, "title": "Workers", "type": "integer"},
"database": {"$ref": "#/$defs/DatabaseConfiguration"}}, "required": ["database"], "title": "ServiceConfiguration",
"type": "object"}}, "additionalProperties": false, "description": "Global configuration.", "properties": {"name":
{"title": "Name", "type": "string"}, "service": {"$ref": "#/$defs/ServiceConfiguration"}}, "required": ["name", "service"],
"title": "Configuration", "type": "object"}
To sice není moc čitelné, ovšem nic nám nebrání v naformátování JSONu, například oblíbeným nástrojem jq:
{
"$defs": {
"DatabaseConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 5432,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"db": {
"title": "Db",
"type": "string"
},
"user": {
"title": "User",
"type": "string"
},
"password": {
"title": "Password",
"type": "string"
},
"ssl_mode": {
"default": "prefer",
"title": "Ssl Mode",
"type": "string"
},
"gss_encmode": {
"default": "prefer",
"title": "Gss Encmode",
"type": "string"
},
"ca_cert_path": {
"anyOf": [
{
"format": "file-path",
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"title": "Ca Cert Path"
}
},
"required": [
"db",
"user",
"password"
],
"title": "DatabaseConfiguration",
"type": "object"
},
"ServiceConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Service configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 8080,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"auth_enabled": {
"default": false,
"title": "Auth Enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"workers": {
"default": 1,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0,
"title": "Workers",
"type": "integer"
},
"database": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/DatabaseConfiguration"
}
},
"required": [
"database"
],
"title": "ServiceConfiguration",
"type": "object"
}
},
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {
"name": {
"title": "Name",
"type": "string"
},
"service": {
"$ref": "#/$defs/ServiceConfiguration"
}
},
"required": [
"name",
"service"
],
"title": "Configuration",
"type": "object"
}
6. Export schématu ve formátu OpenAPI
Výše uvedené schéma do určité míry odpovídá specifikaci OpenAPI, se kterým se pravděpodobně čtenáři tohoto článku již setkali. Ovšem do souboru s popisem schématu musíme doplnit další atributy, zejména specifikaci verze OpenAPI, metainformace, referenci na komponenty (což je vlastní popis modelu a vlastně i jediná zajímavá část celého souboru) a taktéž přidáme atribut paths, který bude prázdný – potřebujeme totiž získat jen popis modelu a nikoli i specifikaci koncových bodů REST API.
Zdrojový kód demonstračního příkladu tedy upravíme. Využijeme funkci models_json_schema z balíčku pydantic.json_schema:
from pydantic.json_schema import models_json_schema
Touto funkcí získáme slovník se schématem či schématy. Obsah tohoto slovníku „zabalíme“ do dalšího slovníku, jehož struktura (jména klíčů a typy hodnot) budou odpovídat OpenAPI. A poté se již provede export obsahu slovníku do souboru ve formátu JSON:
with open("schema_12.json", "w") as fout:
_, schemas = models_json_schema(
[(model, "validation") for model in [Configuration]],
ref_template="#/components/schemas/{model}",
)
openapi_schema = {
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0",
},
"components": {
"schemas": schemas.get('$defs'),
},
"paths": {},
}
json.dump(openapi_schema, fout)
Zdrojový kód takto upraveného demonstračního příkladu bude vypadat následovně:
# Knihovna Pydantic
#
# - model s konfigurací obsahující čtyři atributy
# - jeden z atributů je tvořen dalším modelem
# - kontrola obsahu atributů po inicializaci modelu
# - zákaz inicializace modelu s neznámými atributy
# - úprava schématu do podoby OpenAPI
# - export schématu modelu
import json
from typing_extensions import Optional, Self
from pydantic import (
BaseModel,
ConfigDict,
FilePath,
PositiveInt,
model_validator,
)
from pydantic.json_schema import models_json_schema
# PostgreSQL connection constants
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-SSLMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE = "prefer"
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-GSSENCMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE = "prefer"
class ConfigurationBase(BaseModel):
"""Base class for all configuration models that rejects unknown fields."""
model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid")
class DatabaseConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Database configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 5432
db: str
user: str
password: str
ssl_mode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE
gss_encmode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE
ca_cert_path: Optional[FilePath] = None
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_postgres_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check PostgreSQL configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class ServiceConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Service configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 8080
auth_enabled: bool = False
workers: PositiveInt = 1
database: DatabaseConfiguration
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_service_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check service configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class Configuration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Global configuration."""
name: str
service: ServiceConfiguration
def dump(self, filename: str = "configuration.json") -> None:
"""Dump actual configuration into JSON file."""
with open(filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
fout.write(self.model_dump_json(indent=4))
with open("schema_12.json", "w") as fout:
_, schemas = models_json_schema(
[(model, "validation") for model in [Configuration]],
ref_template="#/components/schemas/{model}",
)
openapi_schema = {
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0",
},
"components": {
"schemas": schemas.get('$defs'),
},
"paths": {},
}
json.dump(openapi_schema, fout)
7. Ukázka vyexportovaného schématu před a po jeho naformátování
Opět se podívejme na obsah JSONu, který jsme získali:
{"openapi": "3.0.0", "info": {"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0"}, "components": {"schemas": {"Configuration":
{"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {"name": {"title": "Name", "type": "string"}, "service": {"$ref":
"#/components/schemas/ServiceConfiguration"}}, "required": ["name", "service"],
"title": "Configuration", "type": "object"}, "DatabaseConfiguration":
{"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "title": "Host", "type":
"string"}, "port": {"default": 5432, "exclusiveMinimum": 0, "title": "Port",
"type": "integer"}, "db": {"title": "Db", "type": "string"}, "user": {"title":
"User", "type": "string"}, "password": {"title": "Password", "type": "string"},
"ssl_mode": {"default": "prefer", "title": "Ssl Mode", "type": "string"},
"gss_encmode": {"default": "prefer", "title": "Gss Encmode", "type": "string"},
"ca_cert_path": {"anyOf": [{"format": "file-path", "type": "string"}, {"type":
"null"}], "default": null, "title": "Ca Cert Path"}}, "required": ["db",
"user", "password"], "title": "DatabaseConfiguration", "type": "object"},
"ServiceConfiguration": {"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Service
configuration.", "properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "title":
"Host", "type": "string"}, "port": {"default": 8080, "exclusiveMinimum": 0,
"title": "Port", "type": "integer"}, "auth_enabled": {"default": false,
"title": "Auth Enabled", "type": "boolean"}, "workers": {"default": 1,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0, "title": "Workers", "type": "integer"}, "database":
{"$ref": "#/components/schemas/DatabaseConfiguration"}}, "required":
["database"], "title": "ServiceConfiguration", "type": "object"}}}, "paths":
{}}
Po naformátování je již zřejmé, že se skutečně přibližujeme ke standardnímu OpenAPI:
{
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0"
},
"components": {
"schemas": {
"Configuration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {
"name": {
"title": "Name",
"type": "string"
},
"service": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/ServiceConfiguration"
}
},
"required": [
"name",
"service"
],
"title": "Configuration",
"type": "object"
},
"DatabaseConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 5432,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"db": {
"title": "Db",
"type": "string"
},
"user": {
"title": "User",
"type": "string"
},
"password": {
"title": "Password",
"type": "string"
},
"ssl_mode": {
"default": "prefer",
"title": "Ssl Mode",
"type": "string"
},
"gss_encmode": {
"default": "prefer",
"title": "Gss Encmode",
"type": "string"
},
"ca_cert_path": {
"anyOf": [
{
"format": "file-path",
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"title": "Ca Cert Path"
}
},
"required": [
"db",
"user",
"password"
],
"title": "DatabaseConfiguration",
"type": "object"
},
"ServiceConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Service configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 8080,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"auth_enabled": {
"default": false,
"title": "Auth Enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"workers": {
"default": 1,
"exclusiveMinimum": 0,
"title": "Workers",
"type": "integer"
},
"database": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/DatabaseConfiguration"
}
},
"required": [
"database"
],
"title": "ServiceConfiguration",
"type": "object"
}
}
},
"paths": {}
}
8. První pokus o načtení schématu do SwaggerEditoru
V dalším kroku se pokusíme schéma uvedené v předchozí kapitole přenést například do interaktivního Swagger editoru, jehož volně použitelná varianta je dostupná na adrese https://editor.swagger.io/. Výsledný Swagger s popisem schématu bude vypadat následovně (provede se převod do YAMLu, to je ovšem jen drobný detail):
To je sice poměrně velký krok dopředu k čitelné dokumentaci, ovšem současně Swagger editor ohlásí několik chyb v našem schématu:
9. Změna atributu exclusiveMinimum na minimum
SwaggerEditor korektně ohlásil chybu v použití atributu exclusiveMinimum. Ten má totiž odlišný význam, než v jakém je použit – je to totiž pravdivostní hodnota, která určuje, zda specifikované minimum určuje otevřený nebo uzavřený interval (tedy „kromě limitní hodnoty“ nebo „včetně limitní hodnoty“). V OpenAPI 3.0.0 tedy potřebujeme zaměnit jméno atributu exclusiveMinimum na minimum, a to (obecně) rekurzivně pro všechny uzly v popisu schématu. Tuto operaci lze provést ještě před exportem schématu do JSONu, a to následující funkcí:
def recursive_update(original: dict) -> dict:
new = {}
for key, value in original.items():
if isinstance(value, dict):
new[key] = recursive_update(original[key])
elif key == "exclusiveMinimum":
new["minimum"] = value
else:
new[key] = value
return new
Zdrojový kód s našim modelem i instrukcemi pro export jeho schématu upravíme do následující podoby:
# Knihovna Pydantic
#
# - model s konfigurací obsahující čtyři atributy
# - jeden z atributů je tvořen dalším modelem
# - kontrola obsahu atributů po inicializaci modelu
# - zákaz inicializace modelu s neznámými atributy
# - úprava schématu do podoby OpenAPI
# - řešení atributu exclusiveMinimum
# - export schématu modelu
import json
from typing_extensions import Optional, Self
from pydantic import (
BaseModel,
ConfigDict,
FilePath,
PositiveInt,
model_validator,
)
from pydantic.json_schema import models_json_schema
# PostgreSQL connection constants
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-SSLMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE = "prefer"
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-GSSENCMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE = "prefer"
class ConfigurationBase(BaseModel):
"""Base class for all configuration models that rejects unknown fields."""
model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid")
class DatabaseConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Database configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 5432
db: str
user: str
password: str
ssl_mode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE
gss_encmode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE
ca_cert_path: Optional[FilePath] = None
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_postgres_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check PostgreSQL configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class ServiceConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Service configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 8080
auth_enabled: bool = False
workers: PositiveInt = 1
database: DatabaseConfiguration
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_service_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check service configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class Configuration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Global configuration."""
name: str
service: ServiceConfiguration
def dump(self, filename: str = "configuration.json") -> None:
"""Dump actual configuration into JSON file."""
with open(filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
fout.write(self.model_dump_json(indent=4))
def recursive_update(original: dict) -> dict:
new = {}
for key, value in original.items():
if isinstance(value, dict):
new[key] = recursive_update(original[key])
elif key == "exclusiveMinimum":
new["minimum"] = value
else:
new[key] = value
return new
with open("schema_13.json", "w") as fout:
_, schemas = models_json_schema(
[(model, "validation") for model in [Configuration]],
ref_template="#/components/schemas/{model}",
)
schemas = recursive_update(schemas)
openapi_schema = {
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0",
},
"components": {
"schemas": schemas.get('$defs'),
},
"paths": {},
}
json.dump(openapi_schema, fout)
Výsledkem bude JSON se schématem, které bude po exportu vypadat následovně:
{"openapi": "3.0.0", "info": {"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0"}, "components": {"schemas": {"Configuration":
{"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {"name": {"title": "Name", "type": "string"}, "service": {"$ref":
"#/components/schemas/ServiceConfiguration"}}, "required": ["name", "service"],
"title": "Configuration", "type": "object"}, "DatabaseConfiguration":
{"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "title": "Host", "type":
"string"}, "port": {"default": 5432, "minimum": 0, "title": "Port", "type":
"integer"}, "db": {"title": "Db", "type": "string"}, "user": {"title": "User",
"type": "string"}, "password": {"title": "Password", "type": "string"},
"ssl_mode": {"default": "prefer", "title": "Ssl Mode", "type": "string"},
"gss_encmode": {"default": "prefer", "title": "Gss Encmode", "type": "string"},
"ca_cert_path": {"anyOf": [{"format": "file-path", "type": "string"}, {"type":
"null"}], "default": null, "title": "Ca Cert Path"}}, "required": ["db",
"user", "password"], "title": "DatabaseConfiguration", "type": "object"},
"ServiceConfiguration": {"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Service
configuration.", "properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "title":
"Host", "type": "string"}, "port": {"default": 8080, "minimum": 0, "title":
"Port", "type": "integer"}, "auth_enabled": {"default": false, "title": "Auth
Enabled", "type": "boolean"}, "workers": {"default": 1, "minimum": 0, "title":
"Workers", "type": "integer"}, "database": {"$ref":
"#/components/schemas/DatabaseConfiguration"}}, "required": ["database"],
"title": "ServiceConfiguration", "type": "object"}}}, "paths": {}}
Po naformátování schématu nástrojem jq dostaneme tuto čitelnou podobu:
{
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0"
},
"components": {
"schemas": {
"Configuration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {
"name": {
"title": "Name",
"type": "string"
},
"service": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/ServiceConfiguration"
}
},
"required": [
"name",
"service"
],
"title": "Configuration",
"type": "object"
},
"DatabaseConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 5432,
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"db": {
"title": "Db",
"type": "string"
},
"user": {
"title": "User",
"type": "string"
},
"password": {
"title": "Password",
"type": "string"
},
"ssl_mode": {
"default": "prefer",
"title": "Ssl Mode",
"type": "string"
},
"gss_encmode": {
"default": "prefer",
"title": "Gss Encmode",
"type": "string"
},
"ca_cert_path": {
"anyOf": [
{
"format": "file-path",
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "null"
}
],
"default": null,
"title": "Ca Cert Path"
}
},
"required": [
"db",
"user",
"password"
],
"title": "DatabaseConfiguration",
"type": "object"
},
"ServiceConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Service configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 8080,
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"auth_enabled": {
"default": false,
"title": "Auth Enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"workers": {
"default": 1,
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Workers",
"type": "integer"
},
"database": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/DatabaseConfiguration"
}
},
"required": [
"database"
],
"title": "ServiceConfiguration",
"type": "object"
}
}
},
"paths": {}
}
10. Druhý pokus o načtení schématu do SwaggerEditoru
Upravené schéma opět načteme do SwaggerEditoru. Výsledkem bude prakticky totožný Swagger, nyní ovšem s korektně nastavenými minimálními hodnotami (pochopitelně jen tam, kde jsme minimum definovali například typem PositiveInt):
Ovšem schéma ještě stále není zcela korektní, na což nás SwaggerEditor upozorní:
11. Špinavý trik s opravou definice volitelných atributů
Poslední chybou, kterou SwaggerEditor detekoval, byla špatná specifikace volitelných atributů modelu, tj. takových atributů, které mají v Pythonu typ Optional (to se převede na „spojení typů“ v uzlu anyOf). Úpravou transformační funkce recursive_update (transformuje jeden popis modelu na jinak strukturovaný popis) můžeme tento problém alespoň částečně obejít, když volitelné atributy nahradíme za přímou definici jejich typu s nastavením příznaku nullable. Výsledkem je korektní popis schématu modelu, i když samotná transformační funkce by si zasloužila mnohem lepší (ale i mnohem delší) implementaci:
def recursive_update(original: dict) -> dict:
new = {}
for key, value in original.items():
# rekurzivní průchod podslovníky
if isinstance(value, dict):
new[key] = recursive_update(original[key])
# řešení volitelných typů
elif key == "anyOf" and isinstance(value, list) and value[1]["type"] == "null":
# jen první typ je konktrétní, ingorovat druhý
val = value[0]["type"]
new["type"] = val
# nový atribut
new["nullable"] = True
# řešení atributu exclusiveMinimum
elif key == "exclusiveMinimum":
new["minimum"] = value
else:
new[key] = value
return new
Opravený zdrojový kód našeho příkladu:
# Knihovna Pydantic
#
# - model s konfigurací obsahující čtyři atributy
# - jeden z atributů je tvořen dalším modelem
# - kontrola obsahu atributů po inicializaci modelu
# - zákaz inicializace modelu s neznámými atributy
# - úprava schématu do podoby OpenAPI
# - řešení atributu exclusiveMinimum
# - řešení volitelné hodnoty
# - export schématu modelu
import json
from typing_extensions import Optional, Self
from pydantic import (
BaseModel,
ConfigDict,
FilePath,
PositiveInt,
model_validator,
)
from pydantic.json_schema import models_json_schema
# PostgreSQL connection constants
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-SSLMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE = "prefer"
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-GSSENCMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE = "prefer"
class ConfigurationBase(BaseModel):
"""Base class for all configuration models that rejects unknown fields."""
model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid")
class DatabaseConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Database configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 5432
db: str
user: str
password: str
ssl_mode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE
gss_encmode: str = POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE
ca_cert_path: Optional[FilePath] = None
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_postgres_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check PostgreSQL configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class ServiceConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Service configuration."""
host: str = "localhost"
port: PositiveInt = 8080
auth_enabled: bool = False
workers: PositiveInt = 1
database: DatabaseConfiguration
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_service_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check service configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class Configuration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Global configuration."""
name: str
service: ServiceConfiguration
def dump(self, filename: str = "configuration.json") -> None:
"""Dump actual configuration into JSON file."""
with open(filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
fout.write(self.model_dump_json(indent=4))
def recursive_update(original: dict) -> dict:
new = {}
for key, value in original.items():
# rekurzivní průchod podslovníky
if isinstance(value, dict):
new[key] = recursive_update(original[key])
# řešení volitelných typů
elif key == "anyOf" and isinstance(value, list) and value[1]["type"] == "null":
# jen první typ je konktrétní, ingorovat druhý
val = value[0]["type"]
new["type"] = val
# nový atribut
new["nullable"] = True
# řešení atributu exclusiveMinimum
elif key == "exclusiveMinimum":
new["minimum"] = value
else:
new[key] = value
return new
with open("schema_14.json", "w") as fout:
_, schemas = models_json_schema(
[(model, "validation") for model in [Configuration]],
ref_template="#/components/schemas/{model}",
)
schemas = recursive_update(schemas)
openapi_schema = {
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0",
},
"components": {
"schemas": schemas.get('$defs'),
},
"paths": {},
}
json.dump(openapi_schema, fout)
Výsledkem bude kratší a současně i korektní schéma:
{"openapi": "3.0.0", "info": {"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0"}, "components": {"schemas": {"Configuration":
{"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {"name": {"title": "Name", "type": "string"}, "service": {"$ref":
"#/components/schemas/ServiceConfiguration"}}, "required": ["name", "service"],
"title": "Configuration", "type": "object"}, "DatabaseConfiguration":
{"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "title": "Host", "type":
"string"}, "port": {"default": 5432, "minimum": 0, "title": "Port", "type":
"integer"}, "db": {"title": "Db", "type": "string"}, "user": {"title": "User",
"type": "string"}, "password": {"title": "Password", "type": "string"},
"ssl_mode": {"default": "prefer", "title": "Ssl Mode", "type": "string"},
"gss_encmode": {"default": "prefer", "title": "Gss Encmode", "type": "string"},
"ca_cert_path": {"type": "string", "nullable": true, "default": null, "title":
"Ca Cert Path"}}, "required": ["db", "user", "password"], "title":
"DatabaseConfiguration", "type": "object"}, "ServiceConfiguration":
{"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Service configuration.",
"properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "title": "Host", "type":
"string"}, "port": {"default": 8080, "minimum": 0, "title": "Port", "type":
"integer"}, "auth_enabled": {"default": false, "title": "Auth Enabled", "type":
"boolean"}, "workers": {"default": 1, "minimum": 0, "title": "Workers", "type":
"integer"}, "database": {"$ref":
"#/components/schemas/DatabaseConfiguration"}}, "required": ["database"],
"title": "ServiceConfiguration", "type": "object"}}}, "paths": {}}
Po naformátování do čitelné podoby:
{
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0"
},
"components": {
"schemas": {
"Configuration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {
"name": {
"title": "Name",
"type": "string"
},
"service": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/ServiceConfiguration"
}
},
"required": [
"name",
"service"
],
"title": "Configuration",
"type": "object"
},
"DatabaseConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 5432,
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"db": {
"title": "Db",
"type": "string"
},
"user": {
"title": "User",
"type": "string"
},
"password": {
"title": "Password",
"type": "string"
},
"ssl_mode": {
"default": "prefer",
"title": "Ssl Mode",
"type": "string"
},
"gss_encmode": {
"default": "prefer",
"title": "Gss Encmode",
"type": "string"
},
"ca_cert_path": {
"type": "string",
"nullable": true,
"default": null,
"title": "Ca Cert Path"
}
},
"required": [
"db",
"user",
"password"
],
"title": "DatabaseConfiguration",
"type": "object"
},
"ServiceConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Service configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 8080,
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"auth_enabled": {
"default": false,
"title": "Auth Enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"workers": {
"default": 1,
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Workers",
"type": "integer"
},
"database": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/DatabaseConfiguration"
}
},
"required": [
"database"
],
"title": "ServiceConfiguration",
"type": "object"
}
}
},
"paths": {}
}
12. Třetí (úspěšný) pokus o načtení schématu do SwaggerEditoru
Po načtení nového popisu schématu ve formátu JSON do SwaggerEditoru se již nehlásí žádné chyby a vytvořený interaktivní Swagger (pravá strana) je taktéž vygenerován zcela korektně. Pochopitelně obsahuje pouze popis komponent, ovšem nic dalšího stejně není zapotřebí:
13. Vygenerování dokumentace ve formátu Markdown
V dalším kroku z popisu schématu ve formátu JSON vygenerujeme čitelnou dokumentaci v Markdownu. Pro tento účel existuje několik více či méně kompletních nástrojů. Jedním z nich je i openapi-to-md, který lze nainstalovat přes PIP, do virtuálního prostředí Pythonu atd.:
$ uv add openapi-to-md Using CPython 3.12.10 interpreter at: /usr/bin/python3.12 Creating virtual environment at: .venv Resolved 7 packages in 259ms Prepared 4 packages in 299ms Installed 5 packages in 16ms + click==8.3.1 + jinja2==3.1.6 + markupsafe==3.0.3 + openapi-to-md==0.1.0b2 + pyyaml==6.0.3
Vlastní převod na Markdown proběhne takto:
$ openapi-to-markdown --input_file schema_14_formatted.json filter_paths () Converting /home/ptisnovs/xy/xxx/schema_14_formatted.json to output.md... Conversion complete.
Výsledkem bude soubor ve formátu Markdown, který obsahuje sadu tabulek s popisem komponent (což jsou části našeho modelu):
# Weyland-Yutani Information System ## 🌍 Base URL | URL | Description | |-----|-------------| # 🛠️ APIs --- # 📋 Components ## Configuration Global configuration. | Field | Type | Description | |-------|------|-------------| | name | string | | | service | | | ## DatabaseConfiguration Database configuration. | Field | Type | Description | |-------|------|-------------| | host | string | | | port | integer | | | db | string | | | user | string | | | password | string | | | ssl_mode | string | | | gss_encmode | string | | | ca_cert_path | string | | ## ServiceConfiguration Service configuration. | Field | Type | Description | |-------|------|-------------| | host | string | | | port | integer | | | auth_enabled | boolean | | | workers | integer | | | database | | |
14. Přidání popisků k jednotlivým atributům modelu
Problémem vygenerované dokumentace jsou především chybějící popisy jednotlivých atributů. Ty ovšem můžeme doplnit, a to tak, že každému atributu přímo v definici modelu přiřadíme hodnotu typu Field. To nám umožní, aby měl každý atribut svoje označení (může se lišit od jména ve zdrojovém kódu) a taktéž popisek.
Pro atributy, které mají nastavenou výchozí hodnotu, je to snadné a přímočaré. Řádek:
host: str = "localhost"
se nahradí za:
host: str = Field(
"localhost",
title="Hostname",
description="Database server host or socket directory",
)
U atributů, které nemají nastavenou výchozí hodnotu, je nutné namísto prvního parametru konstruktoru Field zapsat trojtečku (což je zcela legální konstrukce v Pythonu). Opět si uvedeme příklad jednoho atributu z našeho modelu:
password: str
Atribut password nemá žádnou výchozí hodnotu, takže jeho popisek doplníme s využitím trojtečky:
password: str = Field(
...,
title="Password",
description="Password used to authenticate",
)
15. Úplný zdrojový kód příkladu s popsaným modelem
Zdrojový kód obsahující mj. i definici datového modelu, vypadá po všech provedených úpravách následovně:
# Knihovna Pydantic
#
# - model s konfigurací obsahující čtyři atributy
# - jeden z atributů je tvořen dalším modelem
# - kontrola obsahu atributů po inicializaci modelu
# - zákaz inicializace modelu s neznámými atributy
# - úprava schématu do podoby OpenAPI
# - řešení atributu exclusiveMinimum
# - řešení volitelné hodnoty
# - export schématu modelu
import json
from typing_extensions import Optional, Self
from pydantic import (
BaseModel,
Field,
ConfigDict,
FilePath,
PositiveInt,
model_validator,
)
from pydantic.json_schema import models_json_schema
# PostgreSQL connection constants
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-SSLMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE = "prefer"
# See: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-GSSENCMODE
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE = "prefer"
class ConfigurationBase(BaseModel):
"""Base class for all configuration models that rejects unknown fields."""
model_config = ConfigDict(extra="forbid")
class DatabaseConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Database configuration."""
host: str = Field(
"localhost",
title="Hostname",
description="Database server host or socket directory",
)
port: PositiveInt = Field(
5432,
title="Port",
description="Database server port",
)
db: str = Field(
...,
title="Database name",
description="Database name to connect to",
)
user: str = Field(
...,
title="User name",
description="Database user name used to authenticate",
)
password: str = Field(
...,
title="Password",
description="Password used to authenticate",
)
ssl_mode: str = Field(
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_SSL_MODE,
title="SSL mode",
description="SSL mode",
)
gss_encmode: str = Field(
POSTGRES_DEFAULT_GSS_ENCMODE,
title="GSS encmode",
description="This option determines whether or with what priority a secure GSS "
"TCP/IP connection will be negotiated with the server.",
)
ca_cert_path: Optional[FilePath] = Field(
None,
title="CA certificate path",
description="Path to CA certificate",
)
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_postgres_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check PostgreSQL configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class ServiceConfiguration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Service configuration."""
host: str = Field(
"localhost",
title="Host",
description="Service hostname",
)
port: PositiveInt = 8080
port: PositiveInt = Field(
8080,
title="Port",
description="Service port",
)
auth_enabled: bool = Field(
False,
title="Authentication enabled",
description="Enables authentication subsystem",
)
workers: PositiveInt = Field(
1,
title="Number of workers",
description="Number of workers to be started",
)
database: DatabaseConfiguration = Field(
...,
title="Database configuration",
description="Database configuration",
)
@model_validator(mode="after")
def check_service_configuration(self) -> Self:
"""Check service configuration."""
if self.port > 65535:
raise ValueError("Port value should be less than 65536")
return self
class Configuration(ConfigurationBase):
"""Global configuration."""
name: str = Field(
...,
title="Service name",
description="Service name",
)
service: ServiceConfiguration = Field(
...,
title="Service configuration",
description="Service configuration",
)
def dump(self, filename: str = "configuration.json") -> None:
"""Dump actual configuration into JSON file."""
with open(filename, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
fout.write(self.model_dump_json(indent=4))
def recursive_update(original: dict) -> dict:
new = {}
for key, value in original.items():
# rekurzivní průchod podslovníky
if isinstance(value, dict):
new[key] = recursive_update(original[key])
# řešení volitelných typů
elif key == "anyOf" and isinstance(value, list) and value[1]["type"] == "null":
# jen první typ je konktrétní, ingorovat druhý
val = value[0]["type"]
new["type"] = val
# nový atribut
new["nullable"] = True
# řešení atributu exclusiveMinimum
elif key == "exclusiveMinimum":
new["minimum"] = value
else:
new[key] = value
return new
with open("schema_15.json", "w") as fout:
_, schemas = models_json_schema(
[(model, "validation") for model in [Configuration]],
ref_template="#/components/schemas/{model}",
)
schemas = recursive_update(schemas)
openapi_schema = {
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0",
},
"components": {
"schemas": schemas.get("$defs"),
},
"paths": {},
}
json.dump(openapi_schema, fout)
Po spuštění tohoto modifikovaného příkladu získáme popis schématu, který obsahuje i popisky jednotlivých atributů:
{"openapi": "3.0.0", "info": {"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0"}, "components": {"schemas": {"Configuration":
{"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {"name": {"description": "Service name", "title": "Service name",
"type": "string"}, "service": {"$ref":
"#/components/schemas/ServiceConfiguration", "description": "Service
configuration", "title": "Service configuration"}}, "required": ["name",
"service"], "title": "Configuration", "type": "object"},
"DatabaseConfiguration": {"additionalProperties": false, "description":
"Database configuration.", "properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost",
"description": "Database server host or socket directory", "title": "Hostname",
"type": "string"}, "port": {"default": 5432, "description": "Database server
port", "minimum": 0, "title": "Port", "type": "integer"}, "db": {"description":
"Database name to connect to", "title": "Database name", "type": "string"},
"user": {"description": "Database user name used to authenticate", "title":
"User name", "type": "string"}, "password": {"description": "Password used to
authenticate", "title": "Password", "type": "string"}, "ssl_mode": {"default":
"prefer", "description": "SSL mode", "title": "SSL mode", "type": "string"},
"gss_encmode": {"default": "prefer", "description": "This option determines
whether or with what priority a secure GSS TCP/IP connection will be negotiated
with the server.", "title": "GSS encmode", "type": "string"}, "ca_cert_path":
{"type": "string", "nullable": true, "default": null, "description": "Path to
CA certificate", "title": "CA certificate path"}}, "required": ["db", "user",
"password"], "title": "DatabaseConfiguration", "type": "object"},
"ServiceConfiguration": {"additionalProperties": false, "description": "Service
configuration.", "properties": {"host": {"default": "localhost", "description":
"Service hostname", "title": "Host", "type": "string"}, "port": {"default":
8080, "description": "Service port", "minimum": 0, "title": "Port", "type":
"integer"}, "auth_enabled": {"default": false, "description": "Enables
authentication subsystem", "title": "Authentication enabled", "type":
"boolean"}, "workers": {"default": 1, "description": "Number of workers to be
started", "minimum": 0, "title": "Number of workers", "type": "integer"},
"database": {"$ref": "#/components/schemas/DatabaseConfiguration",
"description": "Database configuration", "title": "Database configuration"}},
"required": ["database"], "title": "ServiceConfiguration", "type": "object"}}},
"paths": {}}
Po naformátování získáme poměrně dobře čitelné schéma, které je navíc zcela korektní:
{
"openapi": "3.0.0",
"info": {
"title": "Weyland-Yutani Information System",
"version": "0.3.0"
},
"components": {
"schemas": {
"Configuration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Global configuration.",
"properties": {
"name": {
"description": "Service name",
"title": "Service name",
"type": "string"
},
"service": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/ServiceConfiguration",
"description": "Service configuration",
"title": "Service configuration"
}
},
"required": [
"name",
"service"
],
"title": "Configuration",
"type": "object"
},
"DatabaseConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Database configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"description": "Database server host or socket directory",
"title": "Hostname",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 5432,
"description": "Database server port",
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"db": {
"description": "Database name to connect to",
"title": "Database name",
"type": "string"
},
"user": {
"description": "Database user name used to authenticate",
"title": "User name",
"type": "string"
},
"password": {
"description": "Password used to authenticate",
"title": "Password",
"type": "string"
},
"ssl_mode": {
"default": "prefer",
"description": "SSL mode",
"title": "SSL mode",
"type": "string"
},
"gss_encmode": {
"default": "prefer",
"description": "This option determines whether or with what priority a secure GSS TCP/IP connection will be negotiated with the server.",
"title": "GSS encmode",
"type": "string"
},
"ca_cert_path": {
"type": "string",
"nullable": true,
"default": null,
"description": "Path to CA certificate",
"title": "CA certificate path"
}
},
"required": [
"db",
"user",
"password"
],
"title": "DatabaseConfiguration",
"type": "object"
},
"ServiceConfiguration": {
"additionalProperties": false,
"description": "Service configuration.",
"properties": {
"host": {
"default": "localhost",
"description": "Service hostname",
"title": "Host",
"type": "string"
},
"port": {
"default": 8080,
"description": "Service port",
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Port",
"type": "integer"
},
"auth_enabled": {
"default": false,
"description": "Enables authentication subsystem",
"title": "Authentication enabled",
"type": "boolean"
},
"workers": {
"default": 1,
"description": "Number of workers to be started",
"minimum": 0,
"title": "Number of workers",
"type": "integer"
},
"database": {
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/DatabaseConfiguration",
"description": "Database configuration",
"title": "Database configuration"
}
},
"required": [
"database"
],
"title": "ServiceConfiguration",
"type": "object"
}
}
},
"paths": {}
}
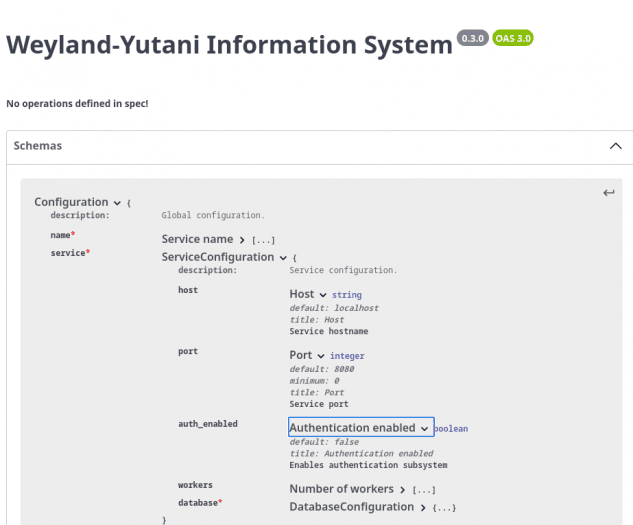
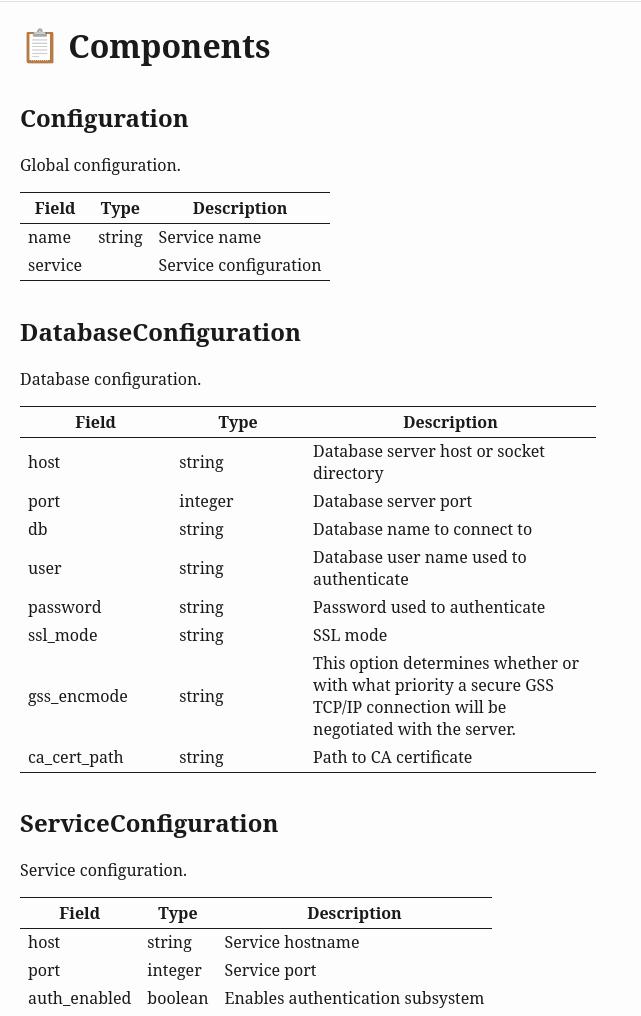
16. Dokument se schématem, které má popsány všechny atributy
Nyní po otevření výše ukázaného schématu ve SwaggerEditoru můžeme vidět, že všechny atributy u sebe mají zobrazeny korektní popisky:
Podobně se „doplnily“ sloupce Description po převodu schématu ve formátu OpenAPI do formátu Markdown (viz obsahy všech tabulek):
# Weyland-Yutani Information System ## 🌍 Base URL | URL | Description | |-----|-------------| # 🛠️ APIs --- # 📋 Components ## Configuration Global configuration. | Field | Type | Description | |-------|------|-------------| | name | string | Service name | | service | | Service configuration | ## DatabaseConfiguration Database configuration. | Field | Type | Description | |-------|------|-------------| | host | string | Database server host or socket directory | | port | integer | Database server port | | db | string | Database name to connect to | | user | string | Database user name used to authenticate | | password | string | Password used to authenticate | | ssl_mode | string | SSL mode | | gss_encmode | string | This option determines whether or with what priority a secure GSS TCP/IP connection will be negotiated with the server. | | ca_cert_path | string | Path to CA certificate | ## ServiceConfiguration Service configuration. | Field | Type | Description | |-------|------|-------------| | host | string | Service hostname | | port | integer | Service port | | auth_enabled | boolean | Enables authentication subsystem | | workers | integer | Number of workers to be started | | database | | Database configuration |
17. Převod na HTML stránku či na jiný typ dokumentu
Posledním krokem, který provedeme, je převod dokumentu s popisem modelu z formátu Markdown do nějakého odlišného formátu vhodného pro přímé zobrazení (na druhou stranu Markdown lze umístit na GitHub pages atd., což může být plně dostačující). Pochopitelně je možné soubor ve formátu Markdown načíst například do textového procesoru, ovšem to není nejvhodnější technologie pro automatizaci generování dokumentace. Namísto toho použijeme populární Pandoc, který je spustitelný z příkazové řádky a nevyžaduje manuální operace:
$ pandoc -s --metadata title="nějaký titulek nebo jen mezera" --from markdown --to html config.md -o config.html
Výsledkem takto provedené konverze je HTML stránka obsahující jak popis modelu, tak i styly atd.:
Obrázek 6: Finální verze dokumentace
18. Závěr
Tvorba dokumentace je většinou dosti nezáživná činnost. Navíc má dokumentace tendenci zastarávat a proto je vhodné se zaměřit na automatizaci pro její generování (samozřejmě tam, kde je to vůbec možné). V případě modelů máme práci usnadněnou, protože vstupem budou přímo zdrojové kódy, což znamená, že by dokumentace neměla zastarávat, pokud bude automaticky z těchto kódů generovaná. Samotná tvorba dokumentace o modelech vyžaduje několik kroků, ovšem ty je možné plně automatizovat a provádět je například v rámci CI/CD pipeline, bez nutnosti manuálních zásahů.
19. Repositář s demonstračními příklady
Demonstrační příklady vytvořené v Pythonu a popsané v dnešním článku i v obou článcích předchozích najdete v repositáři https://github.com/tisnik/most-popular-python-libs/. Následují odkazy na jednotlivé příklady:
20. Odkazy na Internetu
- Validace dat v Pythonu s využitím knihovny Pydantic
https://www.root.cz/clanky/validace-dat-v-pythonu-s-vyuzitim-knihovny-pydantic/ - Validace dat v Pythonu s využitím knihovny Pydantic (2. část)
https://www.root.cz/clanky/validace-dat-v-pythonu-s-vyuzitim-knihovny-pydantic-2-cast/ - Pydantic: domácí stránka
https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/ - Pydantic na GitHubu
https://github.com/pydantic/pydantic - Pydantic na PyPi
https://pypi.org/project/pydantic/ - Introduction to Python Pydantic Library
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python/introduction-to-python-pydantic-library/ - An introduction to Pydantic (with basic example)
https://www.slingacademy.com/article/an-introduction-to-pydantic-with-basic-example/ - Pydantic: Simplifying Data Validation in Python
https://realpython.com/python-pydantic/ - Pydantic: A Guide With Practical Examples
https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/pydantic - Pydantic validators
https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/validators/ - Statické typové kontroly zdrojových kódů Pythonu prováděné nástrojem Mypy
https://www.root.cz/clanky/staticke-typove-kontroly-zdrojovych-kodu-pythonu-provadene-nastrojem-mypy/ - Statické typové kontroly zdrojových kódů Pythonu prováděné nástrojem Mypy (2.část)
https://www.root.cz/clanky/staticke-typove-kontroly-zdrojovych-kodu-pythonu-provadene-nastrojem-mypy-2-cast/ - Statické typové kontroly zdrojových kódů Pythonu prováděné nástrojem Mypy (3)
https://www.root.cz/clanky/staticke-typove-kontroly-zdrojovych-kodu-pythonu-provadene-nastrojem-mypy-3/ - Novinky v typovém systému přidané do Pythonu 3.12
https://www.root.cz/clanky/novinky-v-typovem-systemu-pridane-do-pythonu-3–12/ - Mastering Pydantic – A Guide for Python Developers
https://dev.to/devasservice/mastering-pydantic-a-guide-for-python-developers-3kan - 7 Best Python Libraries for Validating Data
https://www.yeahhub.com/7-best-python-libraries-validating-data/ - Universally unique identifier (Wikipedia)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universally_unique_identifier - UUID objects according to RFC 4122 (knihovna pro Python)
https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/uuid.html#uuid.uuid4 - Object identifier (Wikipedia)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Object_identifier - Digital object identifier (Wikipedia)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_object_identifier - voluptuous na (na PyPi)
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/voluptuous - voluptuous (na GitHubu)
https://github.com/alecthomas/voluptuous - pytest-voluptuous 1.0.2 (na PyPi)
https://pypi.org/project/pytest-voluptuous/ - pytest-voluptuous (na GitHubu)
https://github.com/F-Secure/pytest-voluptuous - schemagic 0.9.1 (na PyPi)
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/schemagic/0.9.1 - Schemagic / Schemagic.web (na GitHubu)
https://github.com/Mechrophile/schemagic - schema 0.6.7 (na PyPi)
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/schema - schema (na GitHubu)
https://github.com/keleshev/schema - XML Schema validator and data conversion library for Python
https://github.com/brunato/xmlschema - xmlschema 0.9.7
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/xmlschema/0.9.7 - jsonschema 2.6.0
https://pypi.python.org/pypi/jsonschema - Tired of Pydantic? Try These 5 Game-Changing Python Libraries
https://developer-service.blog/tired-of-pydantic-try-these-5-game-changing-python-libraries/ - PostgreSQL: 32.1. Database Connection Control Functions
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/libpq-connect.html#LIBPQ-CONNECT-GSSENCMODE - Python type hints: Literals
https://typing.python.org/en/latest/spec/literal.html - YAML
https://yaml.org/ - How to Update Nested Dictionaries in Python Without Overwriting Existing Keys
https://www.pythontutorials.net/blog/updating-nested-dictionaries-when-data-has-existing-key/ - Zpracování dat reprezentovaných ve formátu JSON nástrojem jq
https://www.root.cz/clanky/zpracovani-dat-reprezentovanych-ve-formatu-json-nastrojem-jq/